Understanding FEP
The accidental discovery of PTFE in 1938 by Dr. Roy J. Plunkett has turned out to have the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material. But as PTFE lacks the melt-processability, a need of other fluoropolymers was generated. FEP shares the same basic monomer and is commercially obtained by free-radical polymerization in an aqueous media via addition of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE, CF2=CF2) and hexafluoropropylene (HFP, CF3-CF=CF2).
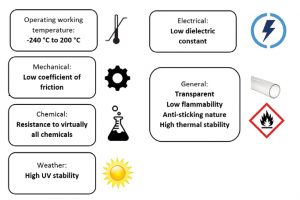
Properties of FEP
Structure of FEP is semi-crystalline, giving it not only a distinct and sharp melting point, but also generally better mechanical properties than those of the amorphous type of polymers. Sterilization of the tubing can be done by gas (EtO), steam (autoclave) and gamma radiation.
Applications
Engineered fluoropolymer lining, tubing and fabricated products for aerospace industry relies on its ability to resist damage from aggressive chemical fuels and withstand wide variation in temperature. Further its non-stickiness nature makes a top choice in food and beverage processing industry. FEP tube is also used for hot sterilizing water transfer in purification system and UV water treatment. FEP tubing’s inability to absorb materials, high chemical inertness and full sterilization capacity makes it ideal choice for sterile filling, diagnostic equipment, cell transfer and laboratory use.
In electrical industry, FEP has well established itself due its low dielectric constant value & high electrical breakdown voltage property.
Retractable coiled FEP tube:
In the recent years, the gradual downfall of PFA retractable coil has been observed due to its incompatibility with solvents. This has increased the consumption of FEP tube which serves greatly because of its high chemical inertness, heat resistance and flexibility. Additionally it’s used
in chemical dispensers, deionised water re-circulators and even in heat exchangers.
How different is it from PTFE and PFA?
Most of the properties vary slightly among these 3 fluoropolymers.
• FEP and PFA can be extruded and thermoformed unlike PTFE.
• FEP has a lower working temperature than PTFE and PFA.
• PFA deforms more under load compared to FEP. This indicates better retractability for FEP.
• Better abrasion resistance of FEP than PFA.
This has resulted in the fact that in the whole family of recently developed fluoropolymers, FEP stands out in its range of applications. Current research is trying on a fluoropolymer which would resist harsh chemicals and is flexible too. This would serve for a large number of the applications and would serve universally.




