Cyber Security is a technological framework which involves a wide range of practices so as to protect the network integrity and prevent program and the data from various attacks.
Introduction
Cyber security is an important challenge in today’s digital era. However, most of the time it gets neglected which results into losses which are beyond compensatory limits. To understand and implement cyber secure system is the need of the hour.
Billions of devices are connected to network. Providing services such as sharing of information, data, and resources increase the risk resulting in data theft, virus, intrusion detection etc.
By adopting the cyber security practices we can create a foolproof system and get lawful access over the network. The field is of growing importance due to increasing reliance on computer systems, including smart phones, televisions and the various tiny devices that constitute the Internet of Things
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber Security is a technological framework which involves a wide range of practices so as to
protect the network integrity and prevent program and the data from various attacks, harm or unintended access.
Cyberspace or Cybernetics
Cyber space refers to the virtual computer world, it is an electronic medium used to form a global computer network to facilitate online communication. It provides a platform for communication and resource sharing from one device to another connected over a network; however it can be misused to perform the unlawful activities if security is not addressed. In cybernetics security is a major challenge
Components of Cyber Spaces
- Physical Infrastructure and Telecommunication devices
- Computer system and related software
- Network connecting computer system and devices
- Network and Networks or Internet
- User & Intermediaries access nodes
- Constituent Data
Why Cybersecurity
With the advancement of network and wireless technologies more and more devices are connected to the network. Further to control the growing devices over the network becomes the challenge. It is observed that most of the time, knowingly or unknowingly trespassing is happening which results into unlawful access over the network.
The only purpose of cybersecurity is to provide secure network which should not only be hack-proof but also protected from various illegal access to the systems over the network. t ensures the devices over the network perform its standard functions, protecting from various thefts data, transactions, anonymous logins, damage to the systems – firmware, etc.
Cybersecurity plays a big role in functional safety. Engineers are starting to realize that their systems can no longer be safe if they are not secure. Also in operational and process technologies cyber security plays a major role in helping smaller suppliers to protect the individual devices over the network. They have less resources, time and money to secure their plants, processes and data.
Impact of Cyber Attacks on Industries
In order to succeed in digital transformation, every industry needs to focus on cyber security as a vital component of every single process and decision they want to take. The ignorance of
cyber security results into cost of a data breach. The data breach in industrial manufacturing is amongst the highest as compared to any other industry. A single breach averages $5.2 million in the industrial sector, according to the 2019 Cost of a Data Breach Report by the Ponemon Institute.
Manufacturers
For the manufacturer achieving cyber resilience involves diligence, good practice and risk management that’s supported by the right security strategy and technologies. With these strategies in place, manufacturers can increase their success and competitiveness by taking advantage of all that Industry 4.0 offers, while controlling the risks.
Cyber attacks in manufacturing targets the smart machines, storage systems and production facilities. It causes disruptions or longer outages, at enormous cost. Unauthorized login may force the unscheduled and sudden shutdown of the expensive equipment such as blast furnace causing a massive damage’ and production loss.
IOT devices and Embedded Systems
With the implementation of I4.0 and IoT, the number of smart devices over the internet are increasing day by day. Hence it becomes a challenge to implement the security in these embedded systems to protect data, identity and services across the entire supply chain. This increases the risk of cyber attacks. Many smart devices have a lifetime of 15 years or more, and are often not easy to access and replace. As many use non-standard hardware and proprietary firmware in embedded systems (such as sensors and pumps), standard computer security software can’t be deployed. One way forward is to use device certificates and public key infrastructure (PKI) architectures. Implementing PKI into embedded systems secures the communication layer, creating a system that verifies the authenticity, configuration, and integrity of connected devices.
Top Cyber Threats to Industries
Insecure API
The use of API used by the end user is managed by cloud service providers; hence the security lies primarily in the hands of the service providers and hence the breaches could happen starting from the authentication to encryption process.
Cloud Abuse
Cloud storage is vulnerable to cyber abuse. With inadequate authentication and registration processes, the cloud will be susceptible to spam emails, criminals, and other malicious attacks.
Malware Attack
Malware attacks can be caused by various reasons, including removable media, file sharing, bundled free software, and the lack of internet security software. To overcome them, organizations need to prepare a strict security compliance strategies and mechanisms.
Hacking
As the Internet of Things takes over, more weak points are created in the computer systems. Besides administer restrictions towards sharing, organizations also need to ensure that no unauthorized activity takes place.
Single Factor Password
There is a large security risk in use of single-factor passwords as it gives intruders easy access to data. Organizations need to be more serious with the passwords by starting to use multi-factor authentication.
IoT
Most devices are connected to the Internet nowadays. As much as the Internet of Things has become useful, its deployment has also brought many concerns, especially in security domain due to inadequate security measures.
Shadow IT Systems
Shadow IT is software used within an organization, but not supported by the company’s central IT system. This has inefficiencies and may be vulnerable to hackers.
Best Practices for Securing Industrial Control Systems
Any industrial control system (ICS) that interacts with the physical world must be secure. Initially, that will mean an assessment to establish the potential hazard and risk, such as that outlined in the health and safety standard IEC 61508. Then, follow the recommendations for providing cyber security technologies and protection for improving control system security, set out in standards such as NIST SP800-82, ISA-99 or IEC 62443. These are essentially best practices for any information security regime.
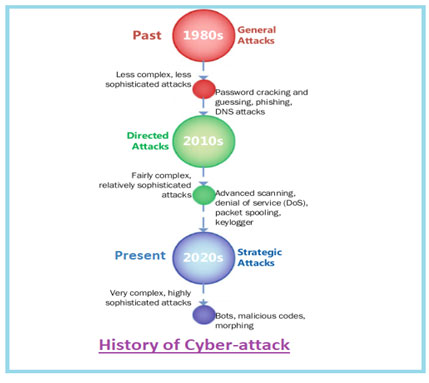
Overview of Cyber Attack
One can easily understand from the history of cyber threats that the threats take many forms and hence to keep the pace with cyber security we need to work on various mitigation strategies, particularly in government and enterprise networks where, in their most innovative form, cyber threats often take aim at secret, political and military assets of a nation, or its people.
Managing Cyber Security Risk
Cyber risk is the probability of exposure or loss resulting from a cyber attack or data breach in an organization. Cyber risks are largely due to the increasing reliance on computers, networks, programs, social media and data globally. To mitigate the security risk over the cyber space, we need to implement strategies at various layers of cyber space such as:
- Protecting user assets
- Protection from attacks, damages and unauthorized access or networks
- Reducing vulnerability in information and ICT system and networks
Tools for Cybersecurity
Every organization needs to take cyber security very seriously. There are innumerable hacking attacks affecting businesses of all sizes. Hackers, malware and viruses are some of the real security threats in the virtual world. It is essential that every company is aware of the dangerous security attacks to keep themselves secure using:
- Passwords
- Anti-virus/Anti-malware Software
- Software patches
- Firewalls
- Two-factor authentication
- Encryption
Implementation Strategies of Cyber Security
Cyber security implementation involves strategic approach and varies from one organization to another. Following are a few key questions which help to define the strategic cyber security implementation:
- When to protect? It means setting the priority of the actions that needed to be taken during system failure so as to achieve fast recovery with minimum downtime
- What to protect? It focuses on designing the mechanism to detect and analyse the threat to avoid failure
- How to protect? It corresponds to the security assurance from various threatening factors by implementing the standard measures and procedures
Conclusion
The use of cyber security can help prevent cyber attacks, data breaches and identity theft and can aid in risk management. When an organization has a strong sense of network security and an effective incident response plan, it is better able to prevent serious cyber attacks.



