When it comes to fabricating plastic parts, there is no dearth of options for the process involved. You have CNC machining, injection molding, 3D printing, extrusion molding, spin casting – and the list goes on. Amongst the many methods, CNC machining and injection molding are two of the most popular techniques employed by manufacturers.
If you are stuck between the two, the following detailed comparison will help.
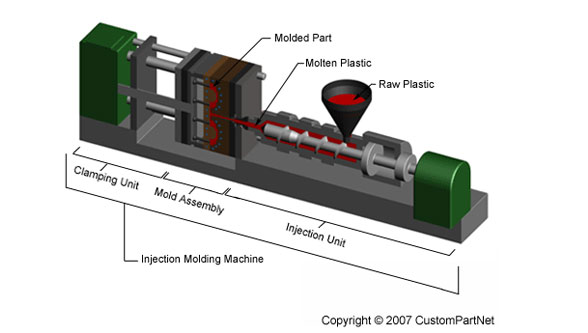
Source: https://www.custompartnet.com/wu/images/im/injectionMolding_machine_overview.png
CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding: Understanding the Processes
The primary difference between CNC machining and injection molding is pretty apparent – the former is about taking away material while the latter involves adding to it.
In simpler words, CNC machining starts with a plastic block that is machined layer by layer in a precise manner to fabricate the desired part. The entire process is controlled by a computer that acts through the CNC router, which imparts accuracy, precision, and high tolerances to the process.
On the other hand, injection molding is pretty much what the name indicates – melting stock material, typically thermoplastics, and injecting it into runners through a high-pressure nozzle. Once the material cools in the molds, the part is ejected, and the process starts afresh
Comparing the Manufacturing Parameters Between CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding
Given the vast difference between the processes, let us compare the difference between CNC machining and injection molding based on multiple metrics.
Speed
When it comes to speed, CNC machining is faster if you are working with low-volume parts. Think of it as a short-term solution for smaller goals considering that molds require anywhere between a couple of weeks to months, which will cause inordinate delays.
Source: https://waykenrm.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/CNC-Plastic-Machining-feature-image.jpg
However, if you wish to manufacture plastic parts consistently, for a longer duration, and in high volumes, injection molding will be a viable solution as you can scale the manufacturing process once the mold is ready. As such, the upfront cost and delay of creating a mold will be offset by its faster manufacturing capabilities.
Cost of Production
To get a fair idea of the cost of production, one needs to consider the cost per part. In this case, we are restricting the factors to volume and speed while decoupling the cost of raw materials.
For a CNC machine, the cost comes up to be cheaper when you are working on a few hundred parts. And when you already have a CNC router machine at your workshop, you only need to invest in the setup costs. However, when the volume increases, the cost-effectiveness hits a plateau.
In contrast, the price per part is significantly low for injection molding as it is. However, mold formation is a significant cost component that accrues right at the initial stages. But once you start producing parts in large volumes (to the effect of 1000 to 5000), this cost distributes with time and brings down the overall cost per unit as an exponential decay.
Material
With CNC machining, you have the option to choose from a great diversity of raw materials for the creation of parts. While it may not seem like much at first glance, it is worth remembering that it is the core material that imparts structural strength and durability to the final product. Hence, if you are working with harder materials such as specific plastics or high-performance plastic material, then CNC machining is the way to go.
With injection molding, material selection hits an upper limit. You have to work with softer plastics like thermoplastics and thermoset resins, which can be melted and molded without compromising on material strength. Most flexible and pliable materials are fabricated through this process.
Tolerance
If you want to maintain precision and accuracy with high tolerances, then a CNC machine can deliver to your expectations. Naturally, the level of control exercised by a computer would involve fewer variables. Plus, the product specifications would be the primary focus of the manufacturing process.
But with injection molding, there exists greater scope and room for common defects such as flow lines, warping, vacuum voids, burn marks, etc., since it considers the tolerances of the mold rather than that of the part.
Design Flexibility
While injection molding offers a high degree of repeatability, it only works in its favor if you are fabricating parts having the same design. If these design specifications were to change in the future, the upfront cost of making the mold would render injection molding completely cost-inefficient as you would once again have to start from scratch.
With CNC machining, adapting to this change would simply involve tweaking the CAD program to incorporate the design changes.
Which Process Should You Choose?
From the above, it is clear that CNC machining and injection molding have two distinct use and applications.
One would consider machining for fabricating walls, overhangs, and other features that involve variability. Similarly, injection molding would be more suited for deep features such as living hinges and square holes that could be tough to replicate with machining. So read through the above comparison and make an informed decision depending on the job at hand.
Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on what you wish to manufacture and its corresponding features.
Article by Vincent Hua
Vincent Hua is the Marketing Manager at TSINFA. He is passionate about helping people understand high-end and complex manufacturing processes. Besides writing and contributing his insights, Vincent is very keen on technological innovation that helps build highly precise and stable CNC Machinery.



